Walk by NASA
Houston, Houston, we got a problem! This expression is now so firmly entered into the everyday life that is perceived as a joke, especially those who live in Houston, as the Mission Control Center is located here.
For tourists, the center was opened in 1992, 16 October, occupying an area of 17,000 square meters. meters. Construction cost $ 75 million each year, the center is visited by about 750 thousand. Man, but only since the opening, the center was visited by over 11 million. Tourists. The Center has long been paid off and brought in 2009 more than $ 242 million.
Today, a walk through the center - internal exposure - shuttle, space toilet, suits of astronauts and more.


Mission Control Center, which bears the official name of NASA's Johnson Space Center, located in the south of Houston, near the military air base - Ellington, and this neighborhood - not without reason, because it is here flew shuttles for inspection, after spaceflight.

After landing in California, the shuttle was loaded onto a transport Boeing, which was carrying him on his back to Houston, sitting on the Air Force base.
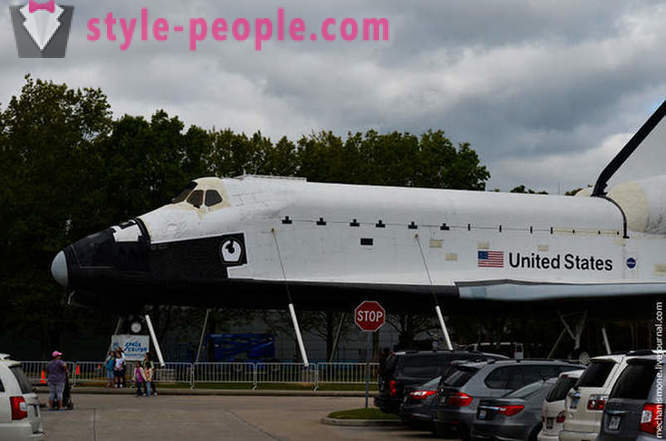

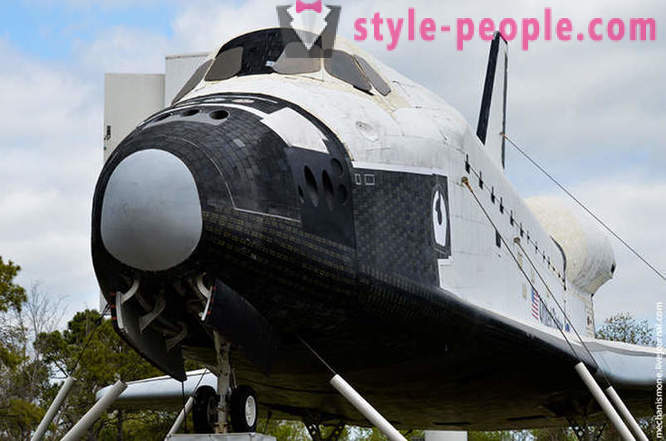
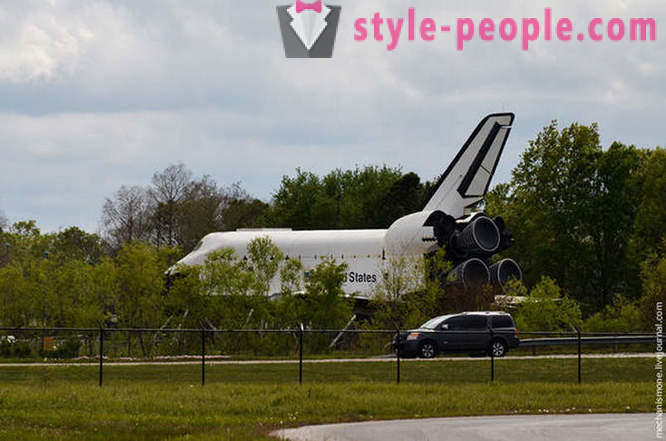
Today, next to the entrance, set last shuttle Explorer. The inner part of preparing for the opening, while still underway work in the near future, it will be possible to get inside. Do not confuse the Explorer between the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and the center in Houston. Florida is set in the mastaba replica 1: 1, in Houston - a real space shuttle.

The preparations for the reception of the shuttle began a long time ago, it was necessary to prepare the site, to raise funds for the repair and improvement of the shuttle for tourists. May 31, 2012 Center announced its full readiness to receive the shuttle.


The inner part of the center is divided into several sections - souvenir shop (where you can buy everything from magnets, ending satellite models), a cinema, a playground, a central hall with suits and the suits, Memory Hall (with photographs of all the groups that have flown in space) but most of the covers of scientific and educational exhibition.

Children's playground, well, where do without Ingres Bords! For children there are a variety of spacecraft in which you can fly, shoot and get to the moon. In addition to entertainment, the center has a staff of teachers who deal with children in astronomy and the sciences. Almost all schools in Houston, visit the center regularly introduces children to exhibits. In addition to children's activities, and there are classes for high school, mostly here taught mathematics and physics. In general, the development of centers for children and students is very wide, despite her young age, the center is looking for talented children and encourages them to get an education up to university full payment.

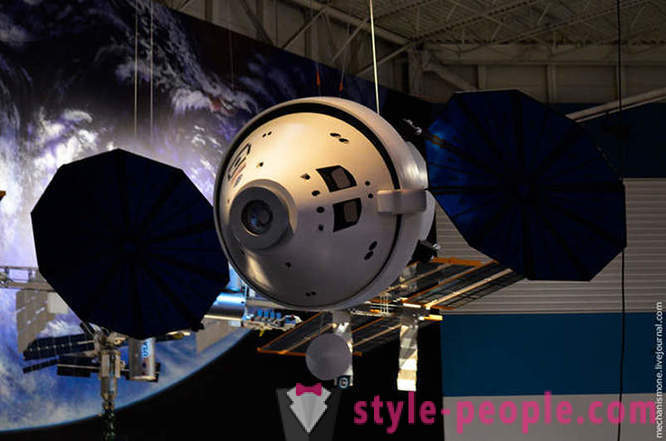
Under the ceiling hang numerous different models of rockets and satellites. The model of the Orion, in a scale of 1:50.

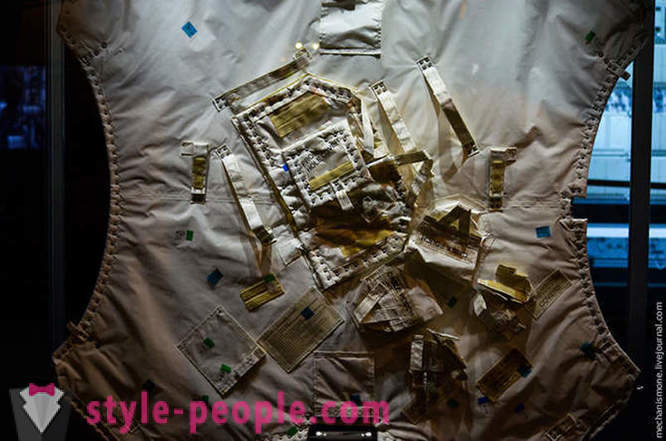
A few interesting moments in the suit, in addition to what he sealed and air supply (everybody knows it), it has a supply of water and food for the astronauts, yet it has a trash bag.

This costume belongs to the first American woman-cosmonaut, Catherine Sullivan. She went into space in 1984 aboard the space shuttle Challenger. Backpack - air supply, additional spotlights were fixed usually on the shoulders (where they do not exist), a small "box" on the chest - water supply, the fan on the right - the temperature indicator, the holes in the bottom of the - for the carbon dioxide emissions from the inside of the suit, a small Case in the upper right, with Velcro from the center closes the hole to connect to the overall system astronaut from supply station (for protracted outputs in space). Suit autonomous within 45 minutes.
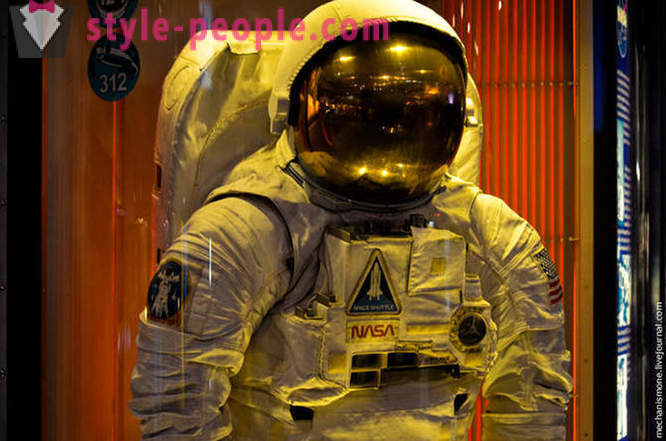

The suit is made of heavy-duty fiberglass, all parts are made for everyday wear standard size that allows you to wear a suit to different astronauts, in addition, all parts of the suit are modular, t. E. To the "body" you can attach the hand of the same size, the feet of another, and helmet - the third. The only thing that is done individually for each - gloves.
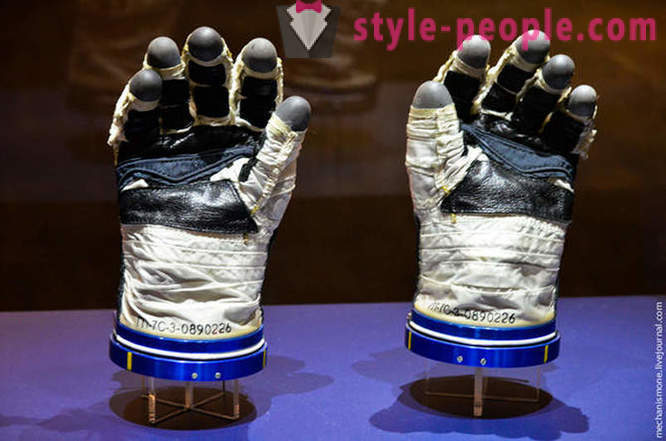

In general, there is a large exhibition of the different costumes and suits different ages, it is very interesting to track the change of design. Left - Donald Sleytana suit, which became an astronaut in 1959, although he went into space only 16 years later, July 15, 1975. Right - casual suit Voltaire Schirra. By the way, he is the only one of the seven original astronauts who could fly directly to Mercury vehicles, Gemini and Apollo.

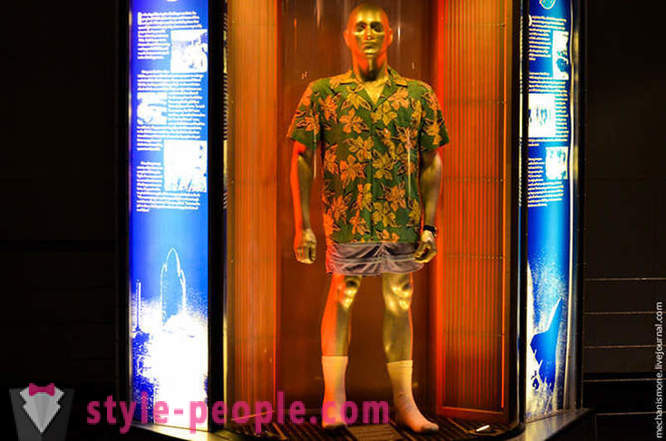
This "costume" is owned by Dick Covey, it was he who spoke with the crew of the Challenger last before the explosion. After the resumption of flights, the first team, which consisted of five astronauts who took a picture inside the shuttle in such shorts and colorful shirts, in memory of the victims.

On the left - a suit MARK-3 is one of the prototypes of the modern suit, designed for protracted spacewalks, the repair or construction of stations. This suit is tight, ie, in contrast to conventional costume flexing only the joints, which brings disadvantages -.. It is hard work, but at the same time it has additional protection from debris, why waste so dangerous - we will consider further for examples. Right - conventional pilot suit such suits worn crew during takeoff and landing of the shuttle.

Costume on the right - after the first four flights into space to get by, and the team stopped wearing tight suits, restrict movement, simple costumes pilots were much more comfortable, but after the disaster with Challenger engineers look changed. In the 1988 year suit for reaching orbit (orange) was introduced, the suit completely sealed and can protect the person in the fire inside the station, while it is soft, it does not restrict the actions of the person.

Modern costumes NASA pilots.

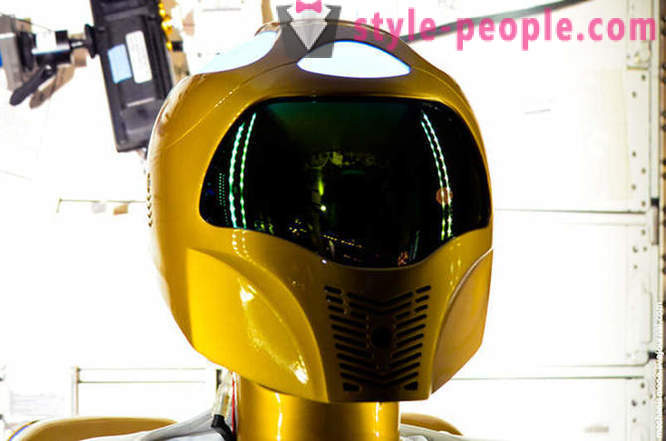
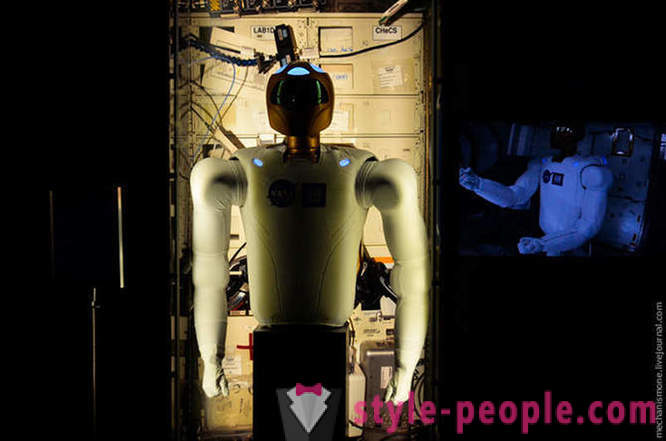
In addition to the suits of astronauts, here is the Robonaut. This robot was designed in Houston, for use in harsh conditions.
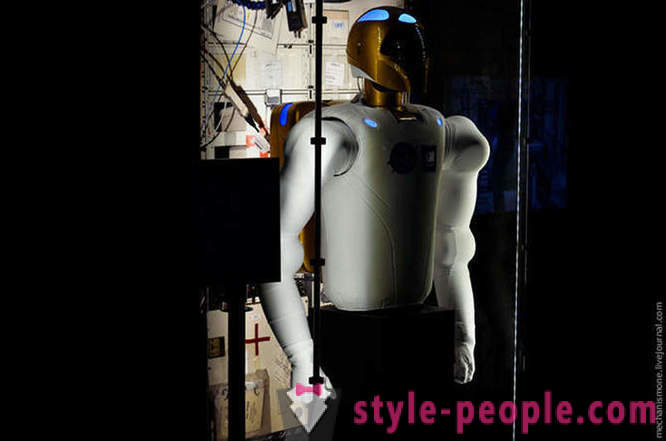
Today there are several versions of Robonaut, a version of R2, introduced in 2011. At this point the robot is under test.

There is also a storage hall, which is a huge wall with pictures of all groups, flown away into space. Wall replenished as flights.

By the way, the astronauts used Omega watches. These clocks were made specifically for space travel, when you create they had to answer tough standards on 11 criteria: withstand high temperature fluctuations, pressure and humidity, operation at high oxygen concentrations, are not afraid to fall, not to provide in case of overload and depressurization, not afraid long vibrations and different acoustic frequencies. So, in the final selection of the competition won the Omega watch, stand, the temperature of up to + -184S 260S blow equivalent to 4.5 tons on the dial area and the centrifuge simulating overload astronauts.

The next part of the internal exposure - education.
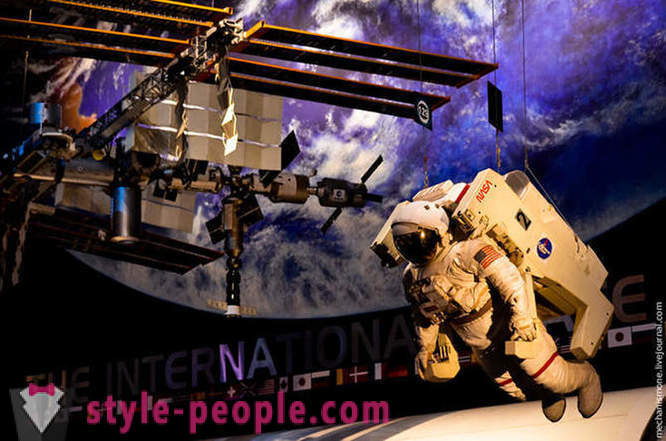
This solar cell space station today. Iron box at the bottom - the packaging in which the battery was flying in orbit.

In fact, ISS. The station today is at an altitude of 402 km above sea level, and its speed of 28,160 km / h. Displacement "live" station is two interior volume 777.

A virtual dock.

Lunokhod.

This wiring international station, which supplies electric power from the battery to the station. The wires are protected by a heavy-duty glass fiber, high-strength steel and special insulators.
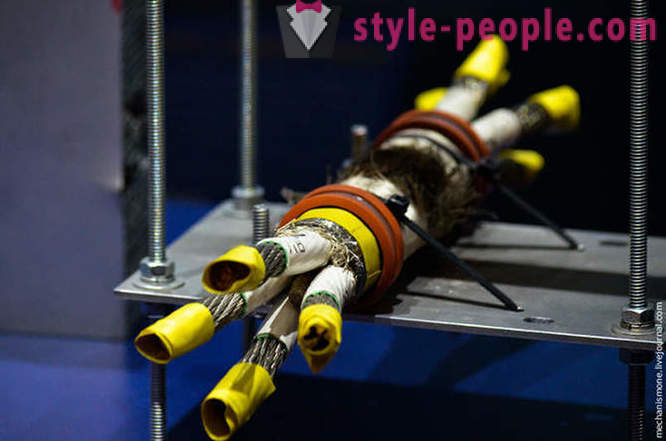

Just above I wrote about the dangers of space debris, and now see why he is so dangerous.
Left - aluminum "shell" thick 102 mm above protecting critical blocks international station, which was a piece of plastic (lying down) at a speed of 6795 m / s. Right - 38 mm aluminum protection, which, according to the tangent was 6x12 mm screw at a speed of 6410 m / s.
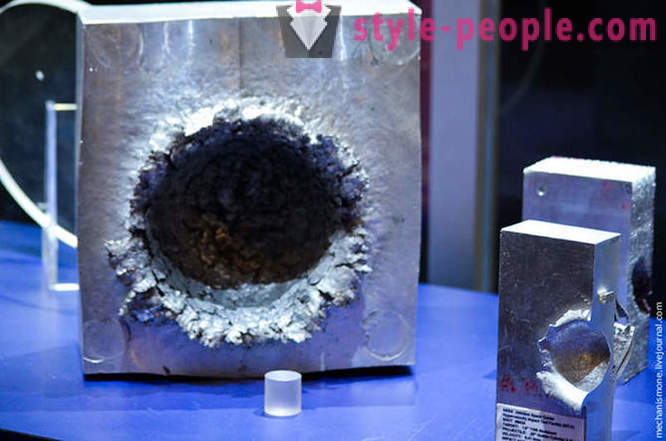

Before the aluminum block to protect the sheet steel is installed, that's what happens to him when he gets all the same Bolt, at a speed of 6410 m / s. After the bolt has struck the sheet it is stuck in an aluminum block. For aluminum is glass, and ceramics.
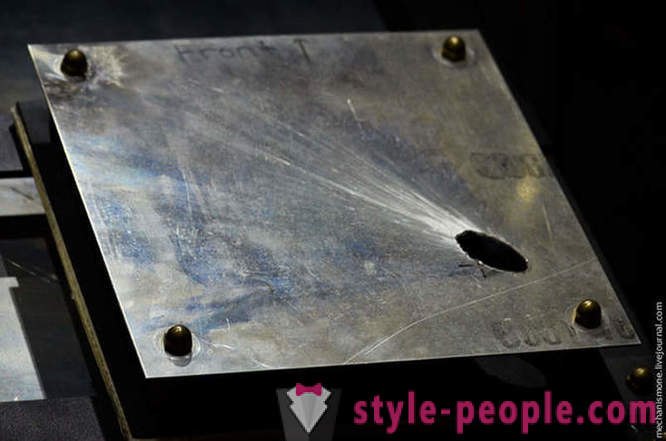

And this protection from the Russian stars, which was pierced aluminum bolt at a speed of 6800 m / s.
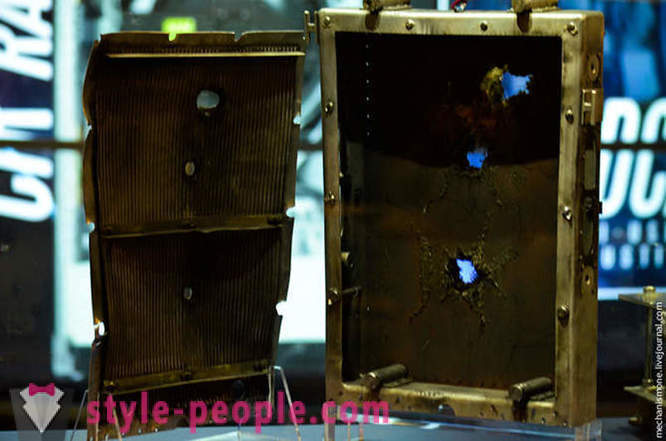

Illuminators also goes. 14 mm Thickness of glass, such cracks in it remain in contact with the bolt at a speed of 7152 m / s. By the way, the station windows consist of four of these glasses for full protection, but then you never know. In the background is the reverse side of the 102-mm aluminum block.
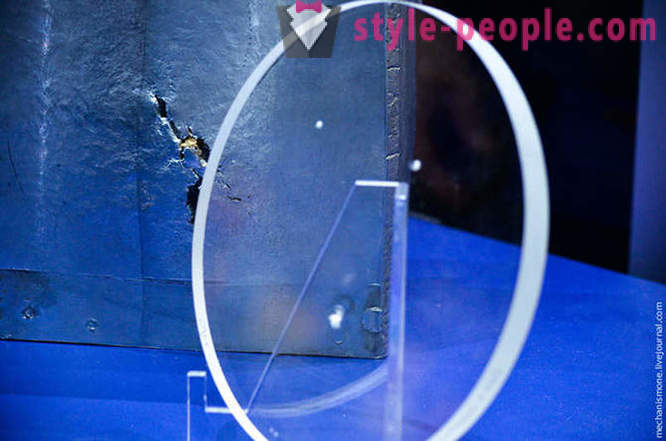

And this the tarpaulin to close the hatches between the docking station during construction. The tarpaulin hung in one of the hatches of the international station for nearly two years. It consists of multiple layers of fiberglass, ceramics, glass and heavy-duty steel fibers. The patches are designed for communications in the construction, but the blue and green stickers - hitting small pebbles and debris, which were discovered after the tarp back on the ground. But no one does not splinter struck protection.

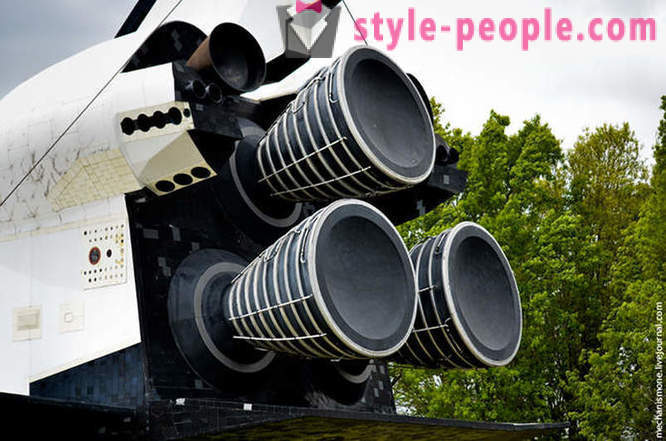
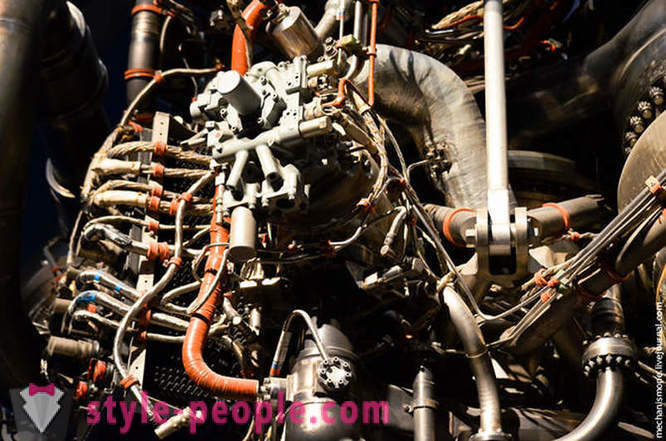
The engine of the shuttle. It is the world's only serial rocket reusable (Buran does not count, that is. To. The project did not really developed). Its weight is about 3200 kg., Such engines have three shuttle, rocket boosters in addition to which the shuttle is attached. Incidentally, this engine has the highest temperature behavior among all engines on the ground, it is capable of operating at temperatures of from -253C to + 3312C (!). The entire engine life - 7 hours, but do not forget that during take-off, it is used just 8.5 minutes.

As the engine uses fuel mixture of liquid oxygen and hydrogen. Oxygen and hydrogen contained in large yellow rocket to which the actual shuttle and "buckled" during takeoff. Three engines reach speeds exceeding the speed of sound 25 times. If we compare the consumption of this engine with the consumption of kerosene aviation turbine of equivalent power, then this engine will consume an equal amount of kerosene Olympic swimming pool every 25 seconds for 8.5 minutes.
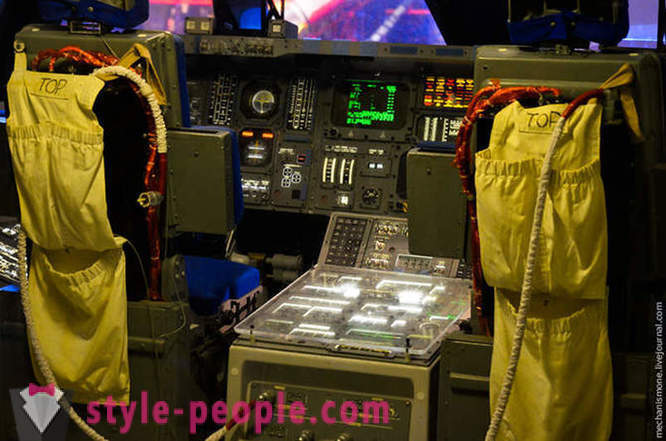
Actually the shuttle. This is a replica made for the training, the size of all the materials and systems within real.

The control cabin.

Helm.
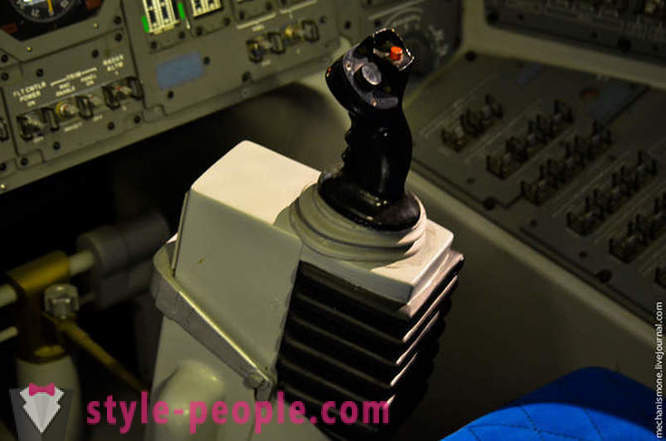

The central panel is larger.

The top panel, for aviation enthusiasts.

Some module behind the pilots.
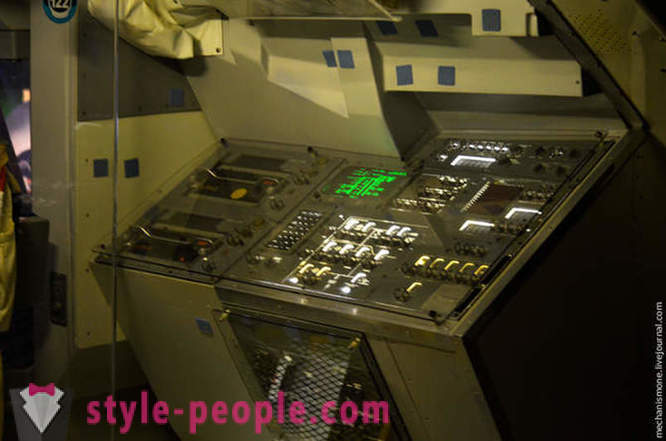
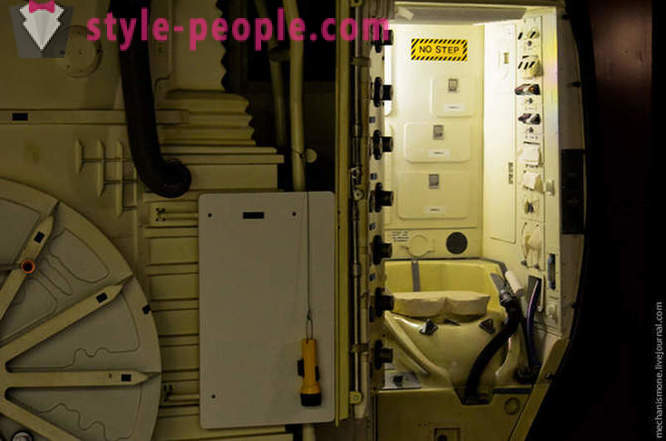


Incision sleeping module shuttle here show a device of this module, and the life of astronauts.

For example so the astronauts are asleep.
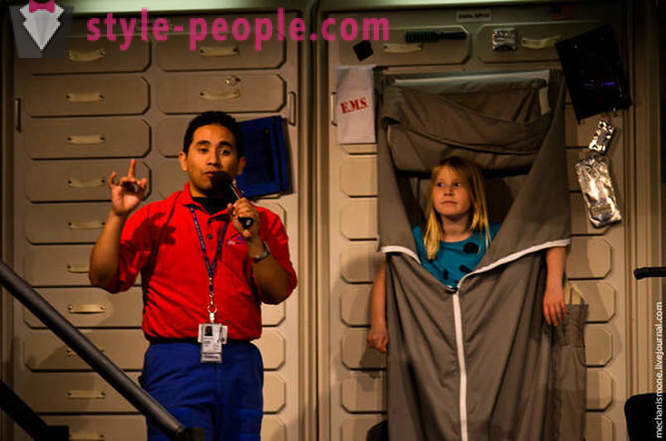

to warm Simulators are hidden behind the wall and put forward as necessary.
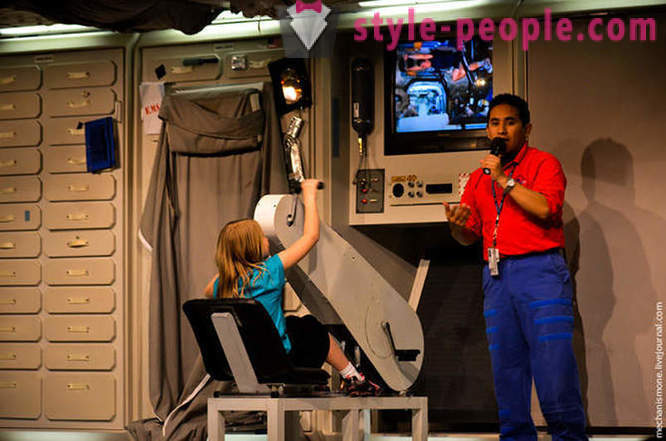

The docking hatch.

But this is a real hatch on Union.
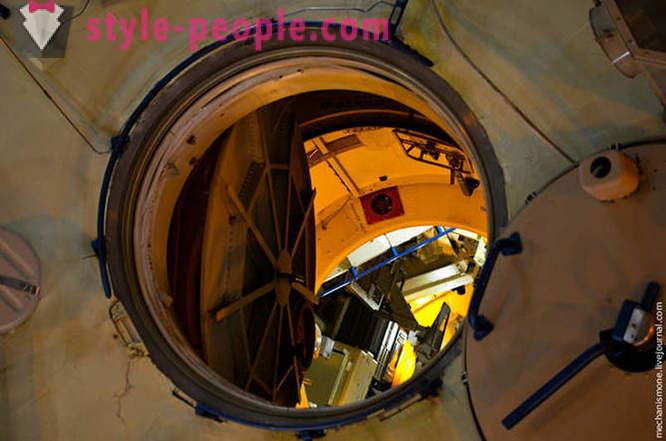

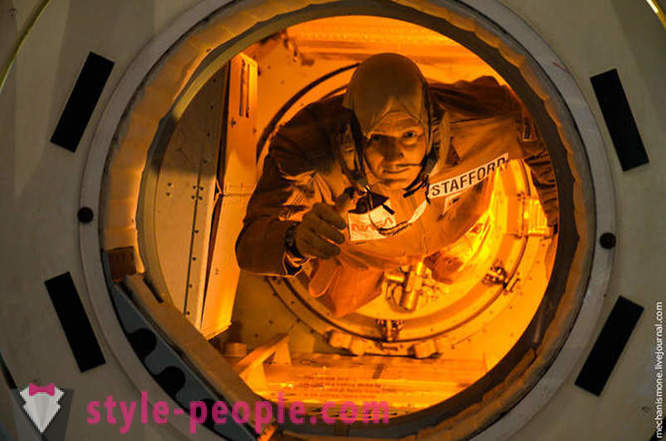
By the way about the dock, then captures the historic moment connections between the Soviet and American units. It was Thomas Stafford opened the door and reached in 1975, Soviet cosmonauts.

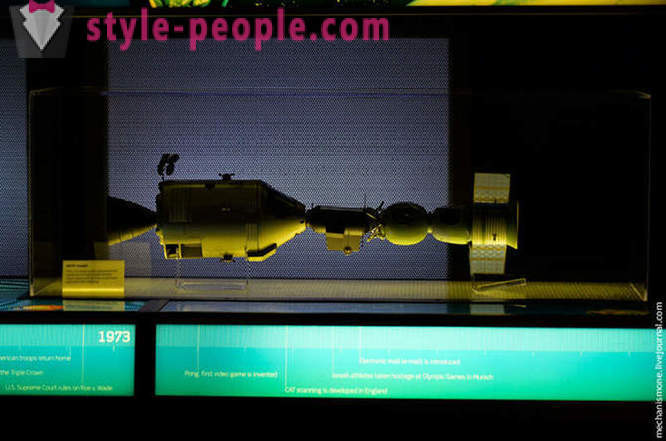
The model 1:25 Apollo command module and a Russian Soyuz after docking.

In general, in a lot of interactivity, the inlet can take iPod, but if you look at the exhibits, then next to each is a digit (in the photograph 10, it can be seen well), so you can listen to on my iPod story of the exhibit. Those who go once there, I advise you to check out and look around, and not just run past, there are a lot of interesting information.


This ends the story.














































