Excursion to the Kurchatov Institute

When I was a kid, one of the first scholars of whom I learned was Igor Kurchatov: a monument to him in the form of a huge, like a fairy-tale hero, head is not rarely in the way of my walks in the native area.
Of course, it attracted the attention and a huge fenced area, which could get very long, always wanted to see what there doing. And last year I shot with high-rise buildings on the street Turquoise, which, thanks to its proximity to the Institute, it was possible to look over the fence.
And here, I had the opportunity not only to look over the fence, but also to visit the territory as a tripper, consider all the closer and torment Officer Scientific Center, which is interesting and detailed account all last week. Here I saw the history and the current activities of the Institute with my own eyes on Europe's first nuclear reactor, to advanced nano- and biotechnologies.

Historical and informative reference
Russian Research Center "Kurchatov Institute" (RRC "KI") was founded in Moscow in 1943 as a Laboratory №2 USSR Academy of Sciences to develop atomic weapons. Since 1960's called the Institute of Atomic Energy. Kurchatov. In 1991 he received the status of the Russian Research Center. The Institute has played a key role in ensuring the country's security. Here, the first in Eurasia nuclear reactor F-1 was established in 1946. In 1949 he developed the first Soviet atomic bomb in 1953 - the world's first thermonuclear bomb, in 1954 - the world's first commercial nuclear power plant in 1955 built the world's first installation of the tokamak, in 1957-58 - the first reactors for icebreakers, submarines and space technology. In 1999, Russia's first synchrotron radiation source was created. Since 2008, a pilot project to create a "Kurchatov Institute" National Research Center. The territory of the RRC "KI" occupies 100 acres and employs 5,000 employees, including 2,000 researchers, 900 doctors and candidates of sciences, 21 members of the Academy of Sciences.
In the RRC "KI" are 5 nuclear research reactors, 14 critical reactor assembly, synchrotron radiation source, nuclear fusion plant Tokmak, Materials Science hot cell complex for the study of irradiated materials, cluster production line for the manufacture of integrated circuits, plant for the separation of isotopes, a set of physical, chemical and radiochemical laboratories, data center-based supercomputer power 120Tflops, laboratory analysis of genomic and synthetic cells, proteins Vai factory and nanofab.
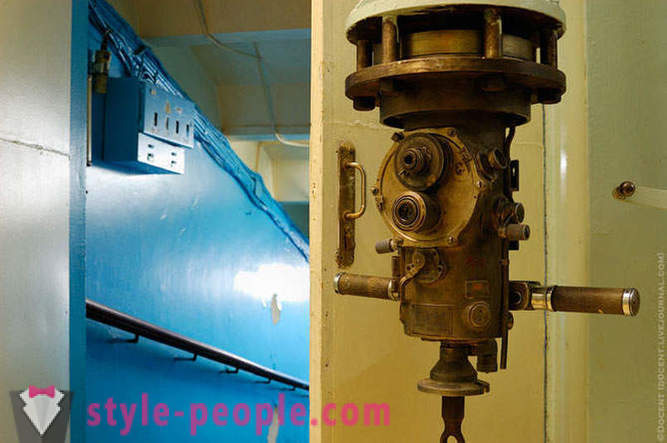
Initially we were shown and told about the reactor F-1 (first physical), on which the December 25, 1946 under the leadership of Kurchatov in the first in Eurasia, self-sustaining fission reaction of uranium was carried out, which allowed to carry out the necessary studies for the design of industrial production of plutonium. The reactor is in operation so far, and his occasional use.
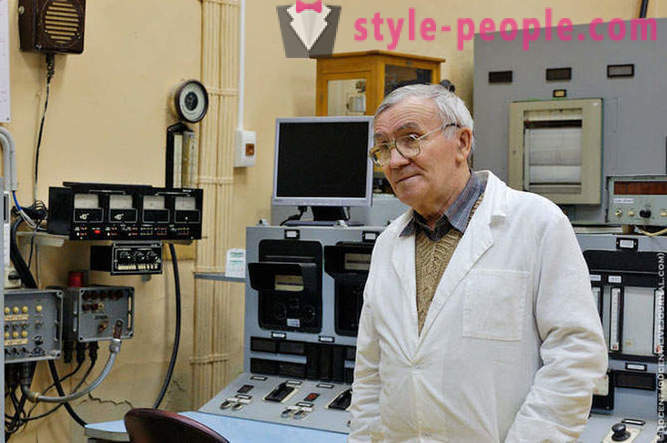

Head engineer reactor F1 Eugene Filipovich Polnikov.

Pokazometry reactor F-1.
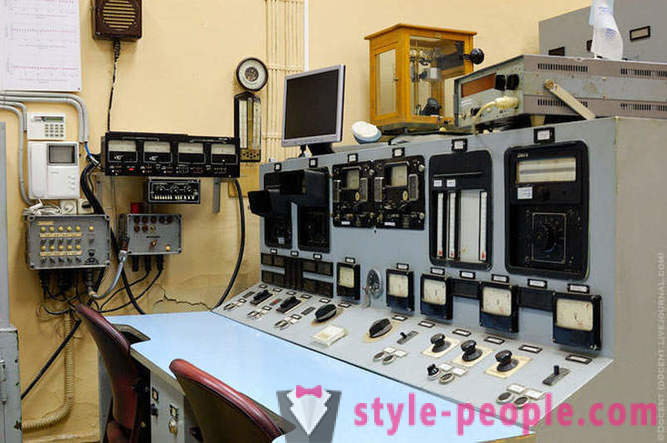

The control unit of the reactor of F-1.
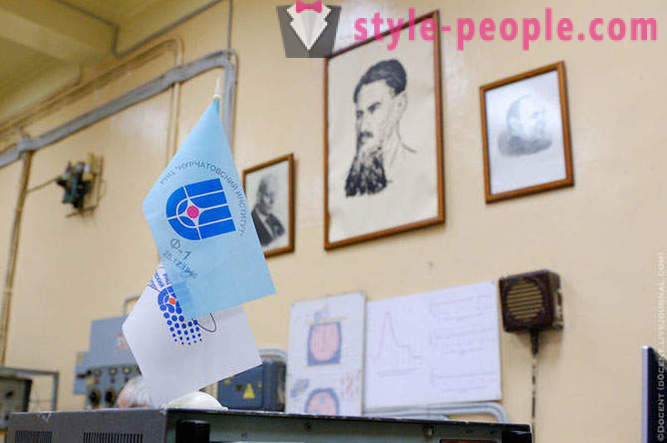
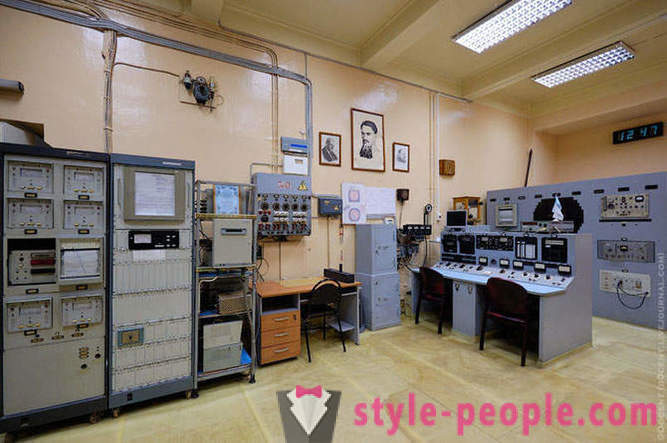
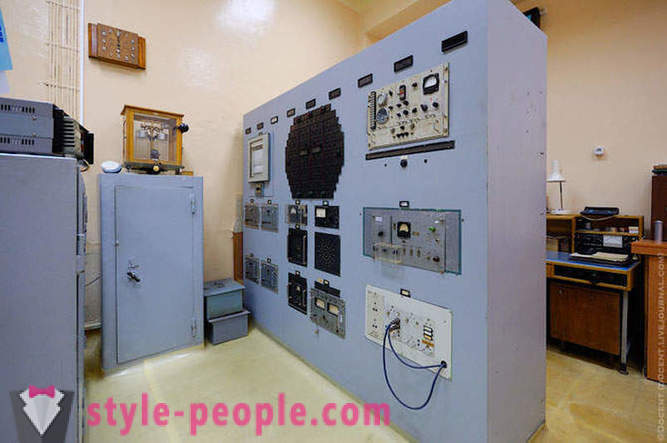



Control Room F-1.
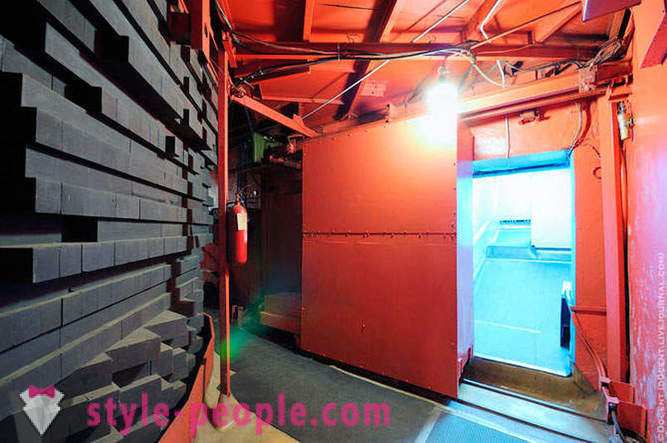

The underground reactor room: Left reactor itself F1, surrounded graphitic blocks, on the right - a thick concrete door opener, which is closed during operation of the reactor.
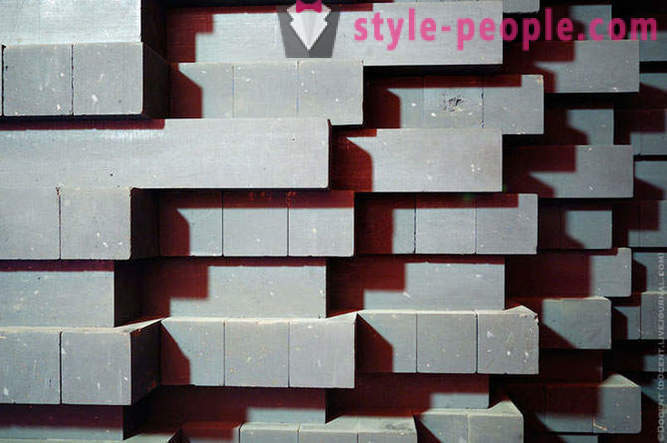

graphite stack.

The radiation background was normal, although we were warned that in this room, it can exceed it 5 times. When the reactor is running, of course, this must not be in the room at all.

In the underground reactor room is a corridor, partitioned concrete blocks, which reduce radiation.

At the entrance to the corridor set periscope presented Kurchatov Institute divers, through it you can look into the upper reactor hall. A real rarity!
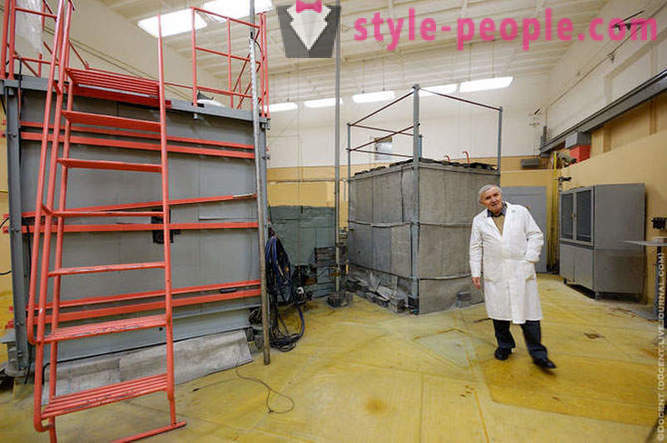

The upper reactor hall. There is a small museum exhibition devoted to the F-1 reactor.
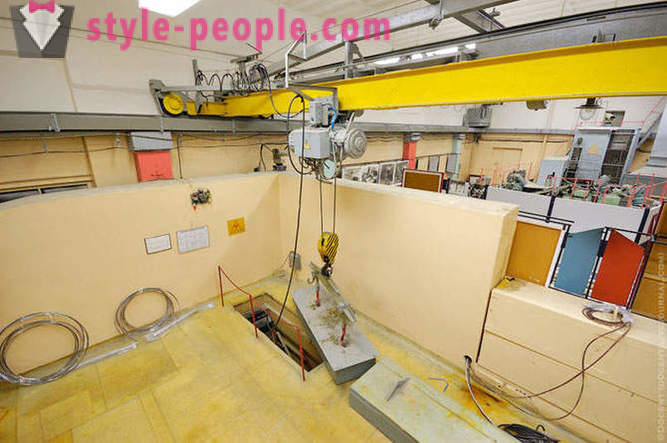

In the reactor hall. There is loaded into a uranium reactor.

Reactor hall.
The next object of the visit was the genomics laboratory. These laboratories are part of a research center of nano-, bio-, information and cognitive sciences and technologies (NBIC technologies). Simply put, there are combined capabilities of many scientific fields and conducted fairly extensive research on the human genome and other organisms. In particular, it carried out whole genome sequencing, carried out research in the field of study of the etiology of cancer and other socially significant diseases.

The product of nano and biotechnology: a matrix, which bear genetic materials studied patients. On the basis of these matrices investigated mutations specific to certain diseases and also carries out extensive genetic characterization ethnic groups.
genomic analyzers Illumina.
jars, flasks, test tubes and other things.
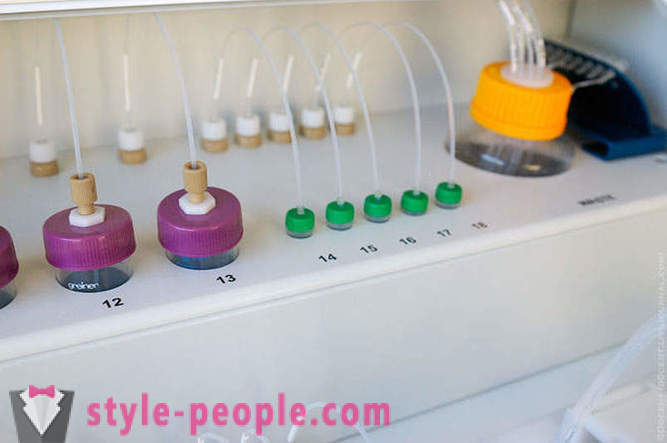
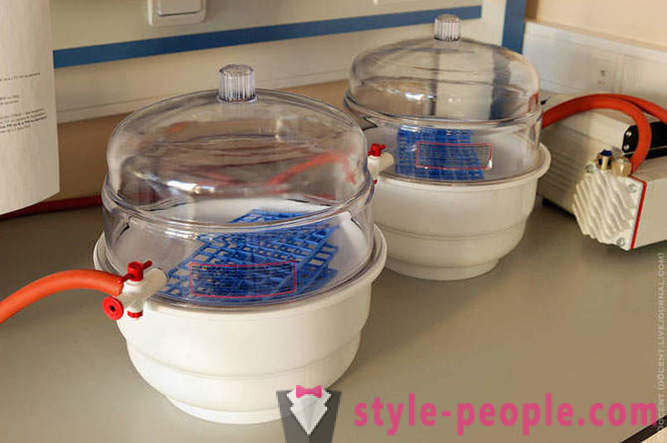
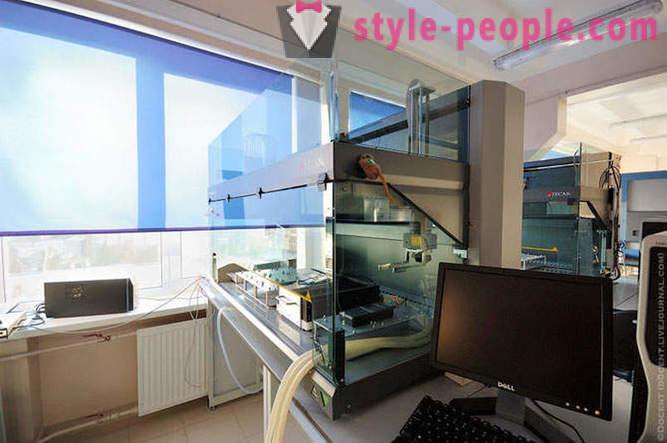




automatic capture system (pipetting) in samples of biological origin and chemical reagents.

Laboratory of protein research.

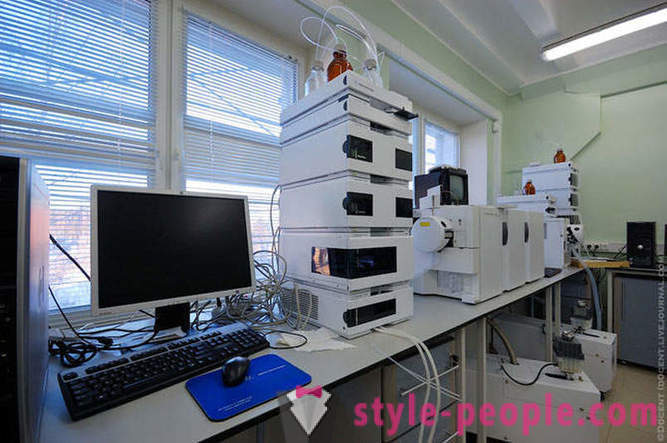
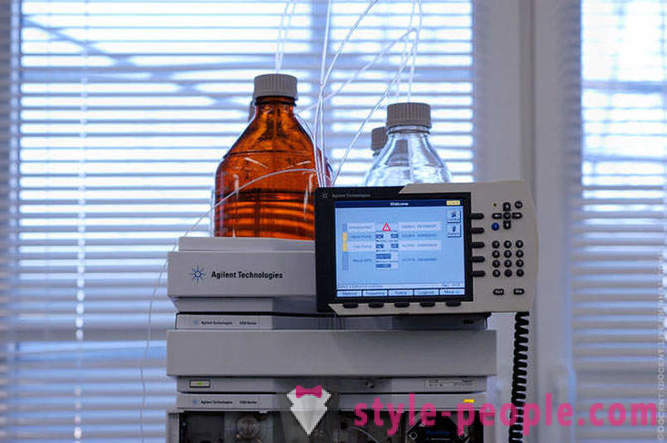
liquid chromatography.

Biological hazard.


And the tube again.

Tools for sampling.

Devices for the amplification (increase in copy number) of nucleic acids.


Laboratory of Molecular Biology.

It is very steep and expensive Titan electron microscope in the laboratory microscopy Kurchatov NBIC-center.
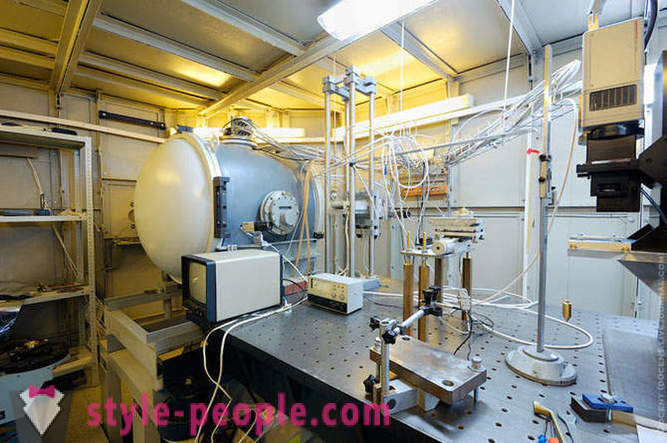

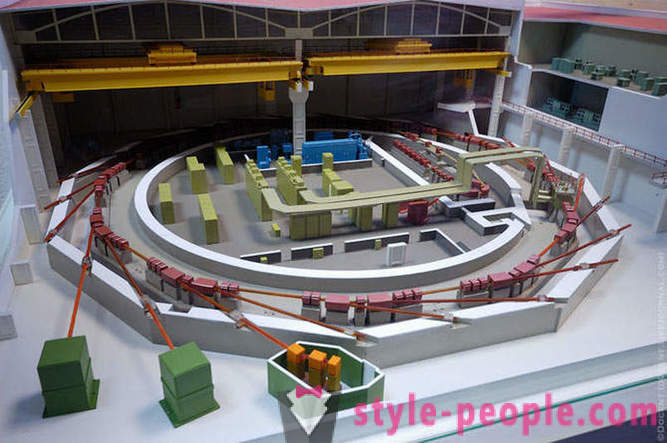
Then we visited the synchrotron. It is an annular chamber in which electrons accelerate and prepared synchrotron radiation (SR) of different spectrum, X-ray, infrared and ultrafialetovogo, which beams are used there are the same for any measurement laboratories. Kurchatov synchrotron began to build in 1986, in 1989, much work has slowed down, and it was only opened in 1999, the same was received and the first beam of radiation from a large storage Siberia-2. Now synchrotron is used as the installation of shared, accepted applications for joint experimentation.
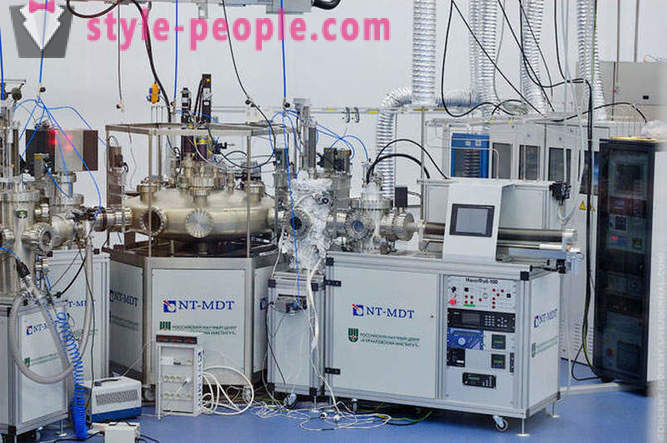
In the synchrotron building, the so-called "clean area" is also an atomic-force microscopes, NANOFAB and installation molecular beam epiktatsii. In the photo - Model synchrotron. To date, the ring was not allowed, due to the fact that the experiment took place on it.

One of the synchrotron laboratories: Station X-ray topography and imaging to the study of crystal structure.

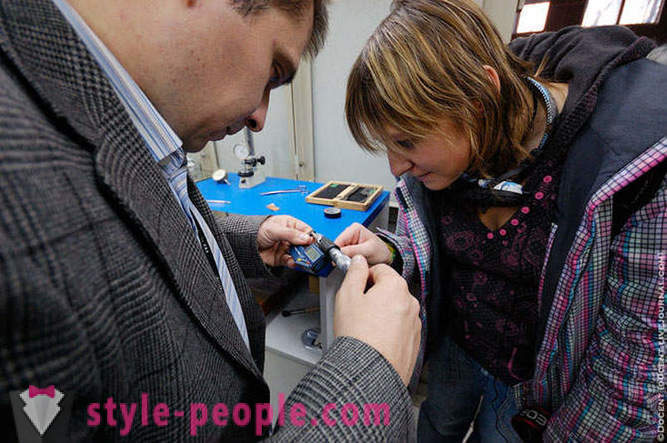
measuring the hair thickness.
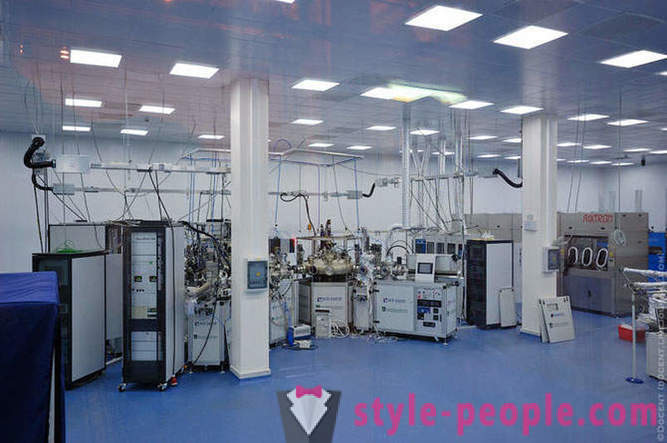

Station X-ray topography.
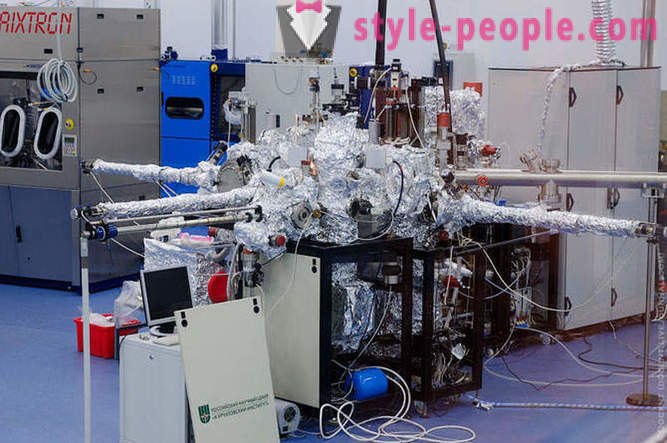
NANOFAB: complex intended for creating electronic circuits elements with dimensions of less than 100 nanometers (nanoelectronics).














































